Getting Goosebumps from Music? Your Brain Has a Special Neural Connection
Getting goosebumps from music is a unique physiological response that only certain people experience, according to scientific research. This phenomenon is linked to specific brain structures and neural connections.
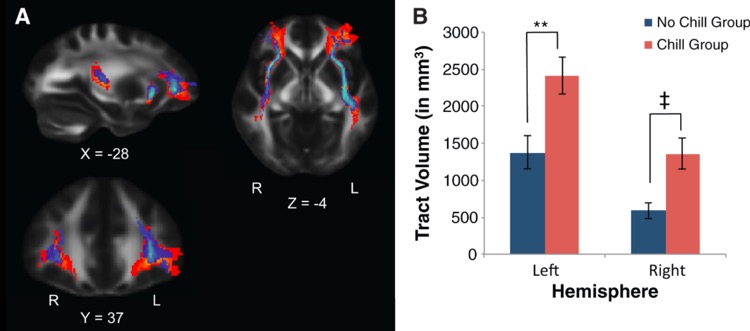
Matthew Sachs, during his studies at Harvard, discovered that people who get music-induced goosebumps have a denser volume of fibers connecting their auditory cortex to emotional processing areas in the brain. Those lacking this neural density simply won't experience the same intense reaction.

Goosebumps with water droplets on skin
The sensation typically includes:
- Shivers down the spine
- Sudden goosebumps formation
- Heightened awareness of the music
- Changes in breathing patterns
- Slowed heart rate
Brain scan showing music-induced goosebumps
Interestingly, some people are entirely unable to experience pleasure from music, despite normal responses to other rewards like money. The initial study examined 20 people selected from 237 participants, with half reporting music-induced goosebumps.
This research has potential implications for treating depression, as the pleasure response to music represents the opposite of depression's inability to experience joy. Music therapy could potentially be used to explore and process emotions more effectively.
The exact percentage of people who experience music-induced goosebumps remains unknown, as research continues at USC's Brain and Creativity Institute, where Sachs is pursuing his PhD in psychology and neuroscience.
These stronger neural connections may also indicate enhanced emotional processing overall, suggesting that people who experience music-induced goosebumps might have generally stronger emotional responses in other areas of life as well.